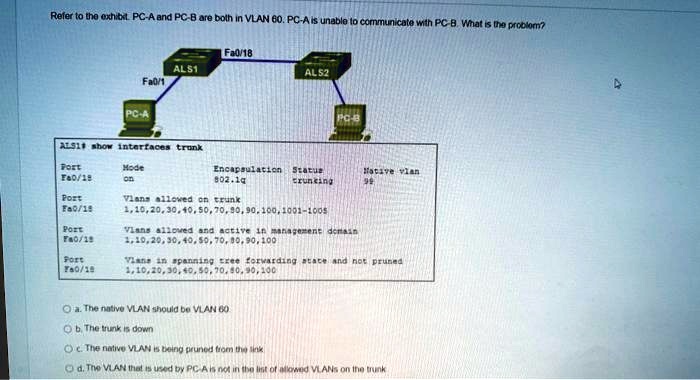
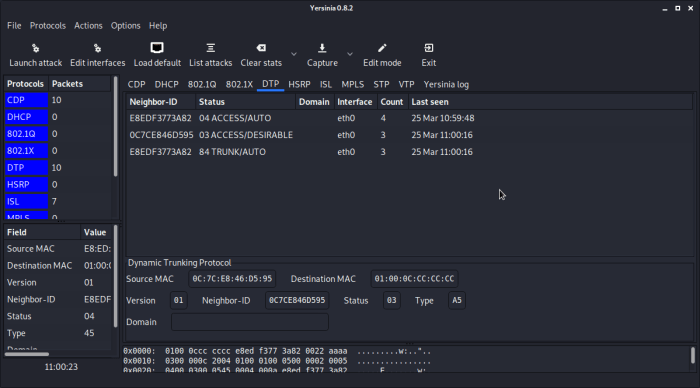
VLANs in spanning tree forwarding state and not pruned present a unique and compelling topic in the realm of network management. Understanding the implications of unpruned VLANs on network performance and the methods to identify and resolve pruning issues is crucial for optimizing network efficiency and ensuring seamless connectivity.
This comprehensive guide delves into the significance of VLAN pruning, its impact on bandwidth utilization and latency, and the best practices for managing VLAN pruning to maintain optimal network performance.
Introduction to VLANs in Spanning Tree Forwarding State and Not Pruned
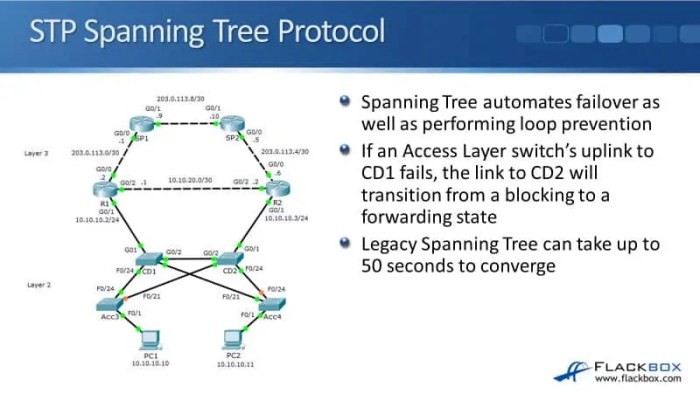
Virtual LAN (VLAN) is a logical segmentation of a network into multiple broadcast domains. Spanning Tree Protocol (STP) is a network protocol that prevents loops in a network by creating a spanning tree, which is a loop-free topology. VLANs play a crucial role in STP forwarding, as they allow for the creation of multiple spanning trees, one for each VLAN.
When a VLAN is not pruned, all switches in the network will forward traffic for that VLAN, regardless of whether or not there are any devices connected to that VLAN on that switch. This can lead to unnecessary traffic and performance degradation.
Impact of VLANs Not Being Pruned on Network Performance
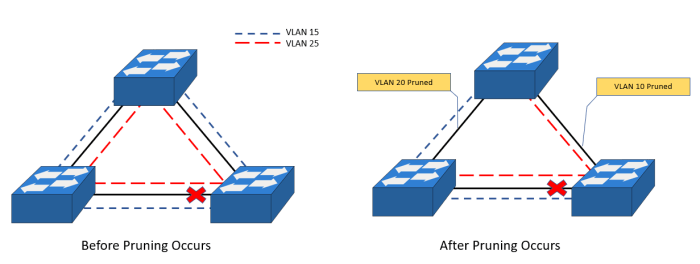
VLANs not being pruned can have a significant impact on network performance. Unpruned VLANs can cause unnecessary traffic to be forwarded, which can lead to bandwidth utilization and latency issues. In addition, unpruned VLANs can make it more difficult to troubleshoot network problems.
For example, if a switch is connected to two VLANs, one of which is not pruned, the switch will forward all traffic for both VLANs, even if there are no devices connected to the unpruned VLAN on that switch. This can lead to unnecessary traffic and performance degradation.
Methods to Identify VLANs in Spanning Tree Forwarding State and Not Pruned
There are a number of tools and techniques that can be used to identify VLANs in STP forwarding state and not pruned. These include:
- Command-line interfaces (CLIs)
- Network management systems (NMSs)
- Packet analyzers
To check the VLAN pruning status using the CLI, you can use the following command:
show spanning-tree vlan
This command will display the STP status for the specified VLAN, including whether or not it is pruned.
Troubleshooting and Resolving VLAN Pruning Issues
If you are experiencing VLAN pruning issues, there are a number of troubleshooting steps that you can take. These include:
- Verifying that the STP settings are correct
- Verifying that the VLAN configurations are correct
- Checking for any errors in the network configuration
If you are unable to resolve the VLAN pruning issue, you may need to contact your network vendor for assistance.
Best Practices for VLAN Pruning Management, Vlans in spanning tree forwarding state and not pruned
There are a number of best practices that you can follow to optimize VLAN pruning. These include:
- Regularly auditing your network to identify any unpruned VLANs
- Monitoring your network for any performance issues that may be caused by unpruned VLANs
- Implementing a VLAN pruning strategy that meets the needs of your network
By following these best practices, you can help to ensure that your network is running at peak performance.
Frequently Asked Questions: Vlans In Spanning Tree Forwarding State And Not Pruned
What are the potential consequences of VLANs not being pruned?
Unpruned VLANs can lead to inefficient bandwidth utilization, increased latency, and potential network loops, which can degrade overall network performance and stability.
How can I identify VLANs in spanning tree forwarding state and not pruned?
Network administrators can use command-line interfaces (CLIs) or network management systems (NMS) to check VLAN pruning status and identify unpruned VLANs.
What are some best practices for VLAN pruning management?
Best practices include regular network audits, monitoring VLAN pruning status, and implementing automated pruning mechanisms to maintain optimal VLAN pruning efficiency.